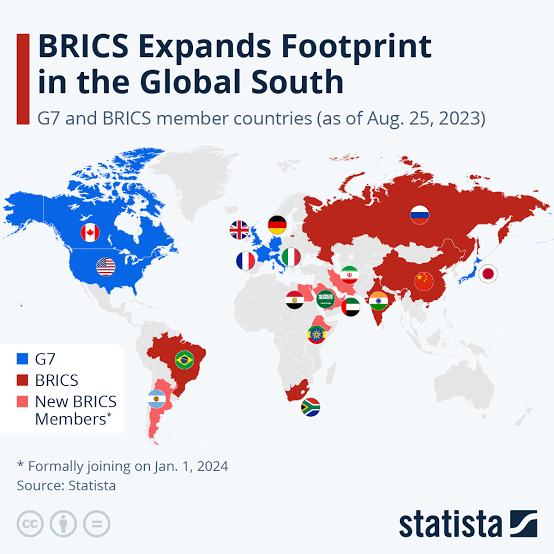
The recent expansion of the BRICS group marks a significant shift in the international political landscape. Saudi Arabia, Egypt, the United Arab Emirates, Iran, and Ethiopia have now officially joined BRICS, heralding a move towards a more inclusive and balanced global governance (CGTN, 2024).
The Growth of BRICS and Multilateralism
Initially formed with Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa, BRICS has evolved into an influential cooperative platform for emerging markets and developing countries. This expansion of adding five more actors signifies a strategic shift, now representing an even more considerable portion of the world’s population and economic output. It is a huge step towards a multipolar world order (Africanews, 2024).
Implications and Impact on Current Conflicts
The addition of these countries to BRICS carries substantial geopolitical implications. This expansion includes major global oil producers and countries positioned near crucial trade chokepoints. It reflects a collective aspiration for a more equitable global governance system and a shift from reliance on the US dollar. The BRICS expansion underlines these countries’ desire for a greater role in international politics and economic decision-making (Council of Councils, 2024).
However, this expansion will bring challenges. The diverse political and economic agendas of the new members add complexity to the group’s dynamics. For example, existing regional rivalries could challenge the group’s cohesion. The inclusion of countries with varied democracy and human rights records also raises questions about the group’s collective stance on these issues (Council of Councils, 2024).
Neoliberal Perspective: Advancing Multilateralism
From a neoliberal perspective, the expansion of BRICS is a positive development towards advancing multilateralism through institutional growth. It shows increasing international cooperation and represents a move towards a more diversified global system. By incorporating a broader range of voices, BRICS is pushing for a global order that better reflects the interests and needs of these countries (CGTN, 2024).
| Group | GDP (Total, in Trillions USD) | Total Military Force (Personnel) | Types of Governments | Population (Total, in Billions) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BRICS | New est. 30+ | 7.7 million + TBD | Mixed | 3.6 + TBD |
| G7 | 40.0 | 4.2 million | Democratic | 0.8 |
| G20 | 69.5 | 10.6 million | Mixed | 5.2 |
| USMCA | 25.2 | 2.9 million | Democratic | 0.5 |
| European Union | 18.5 | 1.5 million | Democratic | 0.45 |
Sources from ChatGPT:
- GDP figures are estimated based on the latest data from the World Bank and IMF reports.
- Total Military Force figures are estimated from global military reports, including SIPRI.
- Population figures are based on the latest estimates from the United Nations population data.

Conclusion on BRICS Expansion
With this expansion, BRICS faces the challenge of harmonizing the diverse political and economic interests of its members. The historical rivalries, such as between Saudi Arabia and Iran, and regional conflicts involving new members like Ethiopia, present a complex diplomatic landscape. Achieving consensus within such a varied group will require delicate balancing and could test the group’s cohesion and effectiveness.
The expanded BRICS also positions itself as a potential rival to established groups like the G7. By representing a significant portion of the global economy and population, the BRICS group is now a more formidable counterbalance to Western-dominated economic and political alliances. This rivalry extends beyond economics into the realms of global governance and security, where the BRICS group’s approach to conflicts and international relations may increasingly challenge Western policies and perspectives.
A New Era of Multipolarity
Ultimately, the BRICS expansion signifies the dawn of a more multipolar world. It represents a shift from a unipolar or Western-centric world order to a landscape where emerging economies unite and exert greater influence. This transition offers both opportunities for new peaceful solutions and complexities that could redefine global conflict dynamics. As BRICS creates its new path, the world watches to see how this reconfiguration influences international politics, economics, and the pursuit of peace and stability.
In this evolving context, the world may witness the emergence of alternative approaches to conflict resolution and international cooperation, shaped by the diverse perspectives within BRICS. However, the group’s ability to navigate internal differences and project a unified stance will be crucial in determining its impact on the global stage. The expansion of BRICS is not just an enlargement of a group but a reflection of changing global narratives, where the voices from different corners of the world demand attention and respect in shaping the future.
References
- ChatGPT. (n.d.). OpenAI. https://chat.openai.com/#
- AfricaNews. (2024, 2 enero). BRICS expansion: Five countries join ranks. Africanews. https://www.africanews.com/2024/01/02/brics-expansion-five-countries-join-ranks/
- Cgtn. (2024, 1 enero). Five countries formally join BRICS. CGTN. https://news.cgtn.com/news/2024-01-01/Five-countries-formally-join-BRICS-1q0oUn0eOTS/p.html
- The BRICS Summit 2023: Seeking an alternate world Order? (s. f.). Council of Councils. https://www.cfr.org/councilofcouncils/global-memos/brics-summit-2023-seeking-alternate-world-order
- Richter, F. (2023, 25 agosto). BRICS expands footprint in the global South. Statista Daily Data. https://www.statista.com/chart/30672/brics-expansion-map/
- Acharya, S. M. S. M. A. A. (2022, 23 mayo). Introducing bipolarity, tripolarity, unipolarity, multipolarity and multiplexity. E-International Relations. https://www.e-ir.info/2022/03/27/introducing-bipolarity-tripolarity-unipolarity-multipolarity-and-multiplexity-in-international-relations/

One response